Cpu Scheduling Round Robin Program
Round Robin Scheduling is a scheduling algorithm used by the system to schedule CPU utilization. This is a preemptive algorithm. There exist a fixed time slice associated with each request called the quantum. The job scheduler saves the progress of the job that is being executed currently and moves to the next job present in the queue when a. Feb 22, 2017 Program for FCFS CPU Scheduling Set 1 Given n processes with their burst times, the task is to find average waiting time and average turn around time using FCFS scheduling algorithm. First in, first out (FIFO), also known as first come, first served (FCFS), is the simplest scheduling algorithm.
What is Round-Robin Scheduling?
The name of this algorithm comes from the round-robin principle, where each person gets an equal share of something in turns. It is the oldest, simplest scheduling algorithm, which is mostly used for multitasking.
In Round-robin scheduling, each ready task runs turn by turn only in a cyclic queue for a limited time slice. This algorithm also offers starvation free execution of processes.
In this Operating system tutorial, you will learn:
Characteristics of Round-Robin Scheduling
Here are the important characteristics of Round-Robin Scheduling:
- Round robin is a pre-emptive algorithm
- The CPU is shifted to the next process after fixed interval time, which is called time quantum/time slice.
- The process that is preempted is added to the end of the queue.
- Round robin is a hybrid model which is clock-driven
- Time slice should be minimum, which is assigned for a specific task that needs to be processed. However, it may differ OS to OS.
- It is a real time algorithm which responds to the event within a specific time limit.
- Round robin is one of the oldest, fairest, and easiest algorithm.
- Widely used scheduling method in traditional OS.
Example of Round-robin Scheduling
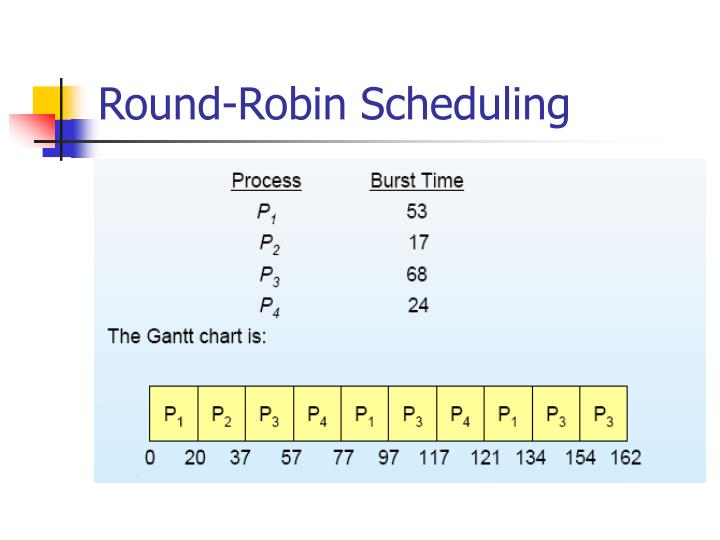
Consider this following three processes| Process Queue | Burst time |
| P1 | 4 |
| P2 | 3 |
| P3 | 5 |
Step 1) The execution begins with process P1, which has burst time 4. Here, every process executes for 2 seconds. P2 and P3 are still in the waiting queue.
Step 2) At time =2, P1 is added to the end of the Queue and P2 starts executing
Step 3) At time=4 , P2 is preempted and add at the end of the queue. P3 starts executing.
Step 4) At time=6 , P3 is preempted and add at the end of the queue. P1 starts executing.
Step 5) At time=8 , P1 has a burst time of 4. It has completed execution. P2 starts execution
Step 6) P2 has a burst time of 3. It has already executed for 2 interval. At time=9, P2 completes execution. Then, P3 starts execution till it completes.
Step 7) Let's calculate the average waiting time for above example.
Advantage of Round-robin Scheduling
Here, are pros/benefits of Round-robin scheduling method:
- It doesn't face the issues of starvation or convoy effect.
- All the jobs get a fair allocation of CPU.
- It deals with all process without any priority
- If you know the total number of processes on the run queue, then you can also assume the worst-case response time for the same process.
- This scheduling method does not depend upon burst time. That's why it is easily implementable on the system.
- Once a process is executed for a specific set of the period, the process is preempted, and another process executes for that given time period.
- Allows OS to use the Context switching method to save states of preempted processes.
- It gives the best performance in terms of average response time.
Disadvantages of Round-robin Scheduling
Here, are drawbacks/cons of using Round-robin scheduling:
- If slicing time of OS is low, the processor output will be reduced.
- This method spends more time on context switching
- Its performance heavily depends on time quantum.
- Priorities cannot be set for the processes.
- Round-robin scheduling doesn't give special priority to more important tasks.
- Decreases comprehension
- Lower time quantum results in higher the context switching overhead in the system.
- Finding a correct time quantum is a quite difficult task in this system.
Worst Case Latency
This term is used for the maximum time taken for execution of all the tasks.
Alice through the looking glass dual audio. Size: 830MB. Quality: 720P.
- dt = Denote detection time when a task is brought into the list
- st = Denote switching time from one task to another
- et = Denote task execution time
Formula:
Summary:
- The name of this algorithm comes from the round-robin principle, where each person gets an equal share of something in turns.
- Round robin is one of the oldest, fairest, and easiest algorithms and widely used scheduling methods in traditional OS.
- Round robin is a pre-emptive algorithm
- The biggest advantage of the round-robin scheduling method is that If you know the total number of processes on the run queue, then you can also assume the worst-case response time for the same process.
- This method spends more time on context switching
- Worst-case latency is a term used for the maximum time taken for the execution of all the tasks.